November is National Diabetes Month, a time to raise awareness about the disease that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says affects 26 million Americans, but certain types can be prevented if one makes lifestyle changes.
The UMHS Endeavour looks at diabetes and what the general public and students at American and Caribbean medical schools can do to help people who already have the disease or are at high risk for developing it.
Facts About Diabetes
The CDC offers the following facts about diabetes (http://www.cdc.gov/features/livingwithdiabetes/).
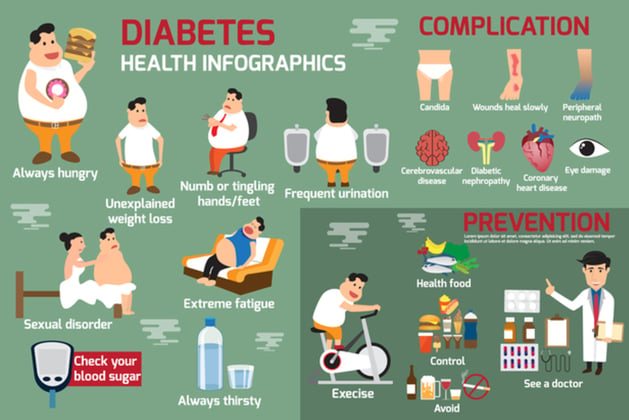
- Left untreated, diabetes can cause heart disease, blindness, kidney failure, and amputations of the foot, leg or toe.
- Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the USA.
- 19 million people are diagnosed with diabetes in the USA each year. 7 million go undiagnosed.
- An estimated 79 million Americans age 20 or older have prediabetes, which “puts them at risk for developing the disease.”
- Prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by learning your risk factors and making lifestyle changes.
What Diabetes Is
A disease causing your blood glucose levels to be above normal. Food is turned into glucose, or sugar. Our bodies store it for energy. Our pancreas, an organ near our stomach, makes the hormone insulin. The insulin helps the glucose get into our bodies cells, but diabetics either cannot make enough insulin or can’t use it as well, thus causing sugar to build up in the blood.
Types of Diabetes
The CDC lists the various types of the disease.
- Type 1 diabetes, which was previously called insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile-onset diabetes, may account for about 5% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes, which was previously called non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or adult-onset diabetes, may account for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that only pregnant women get. If not treated, it can cause problems for mothers and babies. Gestational diabetes develops in 2% to 10% of all pregnancies but usually disappears when a pregnancy is over.
- Other specific types of diabetes resulting from specific genetic syndromes, surgery, drugs, malnutrition, infections, and other illnesses may account for 1% to 5% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
Prediabetes & Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
The CDC notes that prediabetes is an elevated blood glucose level “that is not quite high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes, but is higher than normal.” Many with prediabetes who fail to lose weight or do moderate physical activity often develop type 2 diabetes within 3 years.
Who’s At Risk for Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes?
- People age 45 years of age or older.
- Overweight people.
- Those with a family history of type 2 diabetes.
- Folks who are physically active fewer than three times per week.
- Women who gave birth to a baby that weighed more than 9 pounds.
- Women who had diabetes while pregnant (gestational diabetes).
Helping People at Risk
If you are risk for diabetes or already have prediabetes, there are many things you can do to combat the problem. The CDC has a National Diabetes Prevention Program that is an “evidence-based lifestyle change program for preventing type 2 diabetes.”
Also worth noting is the following is about physical activity reducing the risk of diabetes:
- Regular physical activity can help people cut their risk of developing type 2 diabetes in half.
- The Diabetes Prevention Program research study showed that making modest behavior changes helped participants lose 5% to 7% of their body weight—that is 10 to 14 pounds for a 200-pound person.
- These lifestyle changes reduced the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58% in people with prediabetes.
- Participants work with a lifestyle coach in a group setting to receive a 1-year lifestyle change program that includes 16 core sessions (usually 1 per week) and 6 post-core sessions (1 per month).
For more information, please visit http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/ndep/index.htm
(Top photo). Image: Deposit Photos
About UMHS:
Built in the tradition of the best US universities, the University of Medicine and Health Sciencesfocuses on individual student attention, maintaining small class sizes and recruiting high-quality faculty. We call this unique approach, “personalized medical education,” and it’s what has led to our unprecedented 96% student retention rate, and outstanding residency placements across the US and Canada. UMHS is challenging everything you thought you knew about Caribbean medical schools.

Scott is Director of Digital Content & Alumni Communications Liaison at UMHS and editor of the UMHS Endeavour blog. When he's not writing about UMHS students, faculty, events, public health, alumni and UMHS research, he writes and edits Broadway theater reviews for a website he publishes in New York City, StageZine.com.